Pectra is The Next Big Thing
Picture this: Ethereum, the powerhouse of decentralized applications, is gearing up for another major upgrade. Following the successful Dencun upgrade, the Pectra upgrade is next in line, promising to introduce impactful changes to the Ethereum blockchain. But what's in it for you? Let's dive into the nitty-gritty of Ethereum’s Pectra upgrade and see how it will revolutionize crypto wallets, enhance user experience (UX), and lay the groundwork for future advancements.

What is Pectra Upgrade?
First things first, why the name "Pectra"? It combines two simultaneous upgrades: "Prague" for the execution layer and "Electra" for the consensus layer. This upgrade is like a well-coordinated dance move, ensuring both layers of Ethereum's architecture evolve in harmony. Pectra is shaping up to be a game-changer for Ethereum, even more so than the recent Dencun upgrade. Scheduled for sometime in Q4 2024 or Q1 2025.
Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) for the Pectra Hard Fork
There are around 30 EIPs so far across the EL + CL. Let’s have a look at some of the most important proposals.

1. EIP-7251: Increase the MAX_EFFECTIVE_BALANCE
Overview: EIP-7251 proposes raising the maximum effective balance (MaxEB) for validators from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH. This adjustment allows validators to have a significantly larger portion of their staked ETH actively participating in the consensus process.
Impact:
- With a higher MaxEB, validators can earn rewards on a larger amount of staked ETH.
- Reduces the number of validators needed for a given amount of ETH staked, thus simplifying validator management.
2. EIP-6110: Supply Validator Deposits On-Chain
Overview: EIP-6110 aims to streamline the process for new validators by allowing their deposits to be processed directly on the Consensus Layer (CL) through an in-protocol mechanism.
Impact:
- Reduces the time deposit funds are exposed to potential exploits.
- Simplifies the process of becoming a validator and reduces waiting time.
3. EIP-7594: Peer Data Availability Sampling (PeerDAS)
Overview: EIP-7594 introduces PeerDAS to optimize Layer 2 solutions, focusing on improving data availability sampling.
Impact:
- Optimizes transaction processing and data availability, leading to faster and more efficient Layer 2 solutions.
4. EIP-7553: Separated Payer Transaction (SPT)
Overview: EIP-7553 allows for separating the transaction payer (who pays the gas fees) from the sender (who initiates the transaction and signs it).
Impact:
- Enables more complex access control mechanisms such as multi-signature wallets.
- Supports account abstraction, allowing for innovative wallet management solutions.
5. EIP-7547: Inclusion Lists
Overview: EIP-7547 introduces an inclusion list mechanism to enhance censorship resistance by allowing block proposers to specify transactions that must be included in blocks.
Impact:
- Ensures critical transactions are included in blocks, reducing the risk of transaction censorship.
6. EIP-7545: Verkle Proof Verification Precompile
Overview: EIP-7545 proposes adding a precompiled contract for verifying Verkle proofs, which enhances the efficiency and security of stateless Ethereum.
Impact:
- Facilitates efficient verification of state proofs, contributing to a more scalable and secure Ethereum network.
7. EIP-7377: Migration Transaction
Overview: EIP-7377 allows Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) to deploy code to their addresses once, transforming them into smart contract accounts.
Impact:
- Offers benefits of smart contract features, including multi-signature capabilities and account recovery mechanisms.
8. EIP-7212: Precompile for secp256r1 Curve Support
Overview: EIP-7212 introduces a precompiled contract for efficient verification of signatures using the secp256r1 elliptic curve.
Impact:
- Reduces the cost of verifying signatures using the secp256r1 curve, which is common in security hardware and online services.
9. EIP-7002: Execution Layer Triggerable Withdrawals
Overview: EIP-7002 allows validators to trigger exits and partial withdrawals directly from the execution layer (EL).
Impact:
- Enables more efficient management of validator exits and withdrawals, reducing waiting times and processing complexity.
10. EIP-6914: Reuse Withdrawn Validator Indices
Overview: EIP-6914 optimizes the Beacon Chain by allowing the reuse of validator indices that have been fully withdrawn.
Impact:
- Reduces the storage burden and processing complexity of validator data, supporting long-term network sustainability.
11. EIP-6913: SETCODE Instruction
Overview: EIP-6913 modifies the Beacon Chain to handle withdrawals as "operations" rather than individual objects, improving withdrawal efficiency.
Impact:
- Streamlines the withdrawal process, making it easier to handle large volumes of withdrawals.
12. EIP-6873: Preimage Retention
Overview: EIP-6873 mandates that execution clients retain certain preimages during the transition period from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS).
Impact:
- Ensures critical data is available during the verge period, contributing to a smooth transition between consensus mechanisms.
13. EIP-6800: Unified Verkle Tree State
Overview: EIP-6800 proposes transitioning from the hexary Patricia tree to a Verkle tree structure for state data storage.
Impact:
- Aims to improve the efficiency of state data handling, with implications for self-destruct functionality in contracts.
14. EIP-6466: SSZ Receipts Root
Overview: EIP-6466 combines the transaction root and withdrawal root into a single root to streamline state management.
Impact:
- Reduces complexity and enhances efficiency by consolidating roots.
15. EIP-6465: SSZ Withdrawals Root
Overview: EIP-6465 transitions the encoding of withdrawal roots from the Merkle Patricia Trie (MPT) format to the Simple Serialize (SSZ) format.
Impact:
- Ensures smooth transition to SSZ format while maintaining compatibility with existing MPT-based roots.
16. EIP-6404: SSZ Transactions Root
Overview: EIP-6404 moves the transactions root representation from MPT to SSZ format, aligning with other components of the Ethereum protocol.
Impact:
- Aligns the transactions root encoding with the more recent SSZ format.
17. EIP-6206: EOF - JUMPF and Non-Returning Functions
Overview: EIP-6206 introduces new EVM instructions (JUMPF and RJUMPF) for optimizing function calls, particularly for non-returning functions.
Impact:
- Enhances function call operations, reducing complexity and improving execution performance.
18. EIP-5920: PAY Opcode
Overview: EIP-5920 introduces the PAY opcode for simplifying Ether transfers between contracts and EOAs.
Impact:
- Consolidates multiple operations into a single opcode with built-in security checks to prevent vulnerabilities.
19. EIP-5450: EOF - Stack Validation
Overview: EIP-5450 enhances the EVM by validating the operand stack size during execution of EOF contracts.
Impact:
- Prevents stack-related errors and reduces vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
20. EIP-4762: Statelessness Gas Cost Changes
Overview: EIP-4762 adjusts gas costs to align with the Verkle tree model for storing state data.
Impact:
- Reflects the gas costs incurred under the new Verkle tree structure, optimizing resource allocation.
21. EIP-4444: Bound Historical Data in Execution Clients
Overview: EIP-4444 proposes reducing the storage requirements for nodes by bounding historical data to one year.
Impact:
- Decreases the data storage burden on nodes by allowing older data to be pruned.
22. EIP-4200: Static Relative Jumps
Overview: EIP-4200 introduces new relative jump instructions for EOF contracts, using relative addressing for jump destinations.
Impact:
- Enhances code execution efficiency by using relative addresses for jumps.
23. EIP-3670: EOF - Code Validation
Overview: EIP-3670 implements code validation at contract creation for smart contracts using the EOF format.
Impact:
- Ensures the validity of contract code before it is added to the blockchain.
24. EIP-3540: EOF - EVM Object Format v1
Overview: EIP-3540 introduces the EVM Object Format (EOF) for Ethereum smart contracts, enabling extensible and versioned contract formats.
Impact:
- Facilitates easier upgrades and improvements to the EVM by separating code and data.
25. EIP-3074: AUTH and AUTHCALL Opcodes
Overview: EIP-3074 introduces the AUTH and AUTHCALL opcodes to delegate transaction authorization to smart contracts.
Impact:
- Moves towards making EOAs and contract accounts functionally equivalent, enhancing flexibility in transaction management.
26. EIP-3068: Precompile for BN256 HashToCurve Algorithms
Overview: EIP-3068 introduces a precompiled contract for HashToCurve and Pairing Check operations on the BN256 elliptic curve.
Impact:
- Supports cryptographic protocols like zero-knowledge proofs with efficient curve operations.
27. EIP-2537: Precompile for BLS12-381 Curve Operations
Overview: EIP-2537 integrates BLS12-381 curve operations, enhancing multi-party computation (MPC) functionalities.
Impact:
- Simplifies multi-signature operations and key management, reducing complexity and improving security.
28. EIP-7702: Temporary EOA to smart contract conversion
Overview: EIP-7702, drafted by Vitalik Buterin, introduces a new transaction type that temporarily converts Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) into smart contract wallets. This proposal enhances transaction capabilities while maintaining the original nature of EOAs.
Impact:
- Unlocks smart contract functionalities for EOAs during transactions.
- Allows bundling multiple transactions for efficiency & enables transactions to be paid by another account.
- Grants limited permissions to specific subkeys for enhanced security.
- Provides a more flexible transaction process, potentially reducing gas fees and enhancing overall network efficiency.
A Closer Look at the Security Implications of EIP-3074
As Ethereum evolves, so too do the mechanisms that govern its transactions and user interactions. One significant proposal in the Pectra Upgrade is EIP-3074, which introduces new opcodes—AUTH and AUTHCALL—to enable Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) to delegate transaction signing to designated smart contracts, referred to as "invokers." While this introduces considerable flexibility and functionality, it also presents several critical security considerations that warrant thorough examination.

1. Needed for Trusted Invokers
EIP-3074 allows EOAs to delegate transaction authorization to a smart contract, known as an "invoker," which then processes the transaction on behalf of the EOA. This mechanism introduces several important security considerations:
- Delegation Risk: If the invoker contract is compromised, an attacker could potentially gain control over the EOA's assets. Unlike traditional EOAs, where a single compromised transaction only affects the funds involved, a compromised invoker could jeopardize all assets associated with the EOA. This broadens the risk exposure and highlights the need for stringent security measures for invoker contracts.
- Whitelisting Mechanisms: To mitigate risks, the Ethereum network may implement mechanisms such as whitelists, allowing only trusted users or contracts to act as invokers. This approach aims to limit the potential attack surface by ensuring that only verified and secure invokers can participate in transactions.
2. Replay Attacks
Replay attacks are a significant concern for transactions enabled by EIP-3074:
- Definition: A replay attack occurs when an attacker intercepts and re-broadcasts a valid transaction to perform unauthorized actions or duplicate transactions. Since EIP-3074 involves delegating transaction signing, ensuring that such transactions are protected against replay attacks is crucial.
- Protection Mechanisms: Implementing robust replay protection mechanisms is essential to safeguarding against these attacks. Nonces, which are unique identifiers for each transaction, can prevent reuse. Timestamps can also be employed to ensure transactions are only valid within a specific timeframe, adding another layer of protection.
3. Invoker Contract Vulnerabilities
The security of EIP-3074 hinges on the integrity and robustness of the invoker contracts:
- Vulnerability Risks: The invoker contract itself is a critical component in this system. Vulnerabilities such as reentrancy bugs, where an attacker repeatedly invokes a contract before the previous execution completes, or logic errors, where the contract behaves in unintended ways, could be exploited to drain funds or manipulate transactions.
- Thorough Audits: To mitigate these risks, invoker contracts must undergo comprehensive security audits and reviews. Auditors need to scrutinize the contract code for common vulnerabilities, ensuring that proper safeguards are in place. Regular updates and patches may also be necessary to address emerging threats.
Vitalik Buterin Drafted The EIP-7702 in Just 22 Minutes!
In a remarkable feat of innovation, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin drafted EIP-7702 in just 22 minutes, adding a powerful new dimension to Ethereum's scalability and functionality. This proposal has captivated the Ethereum community and is poised to play a pivotal role in the Pectra upgrade. Here’s a closer look at the key aspects and implications of EIP-7702:
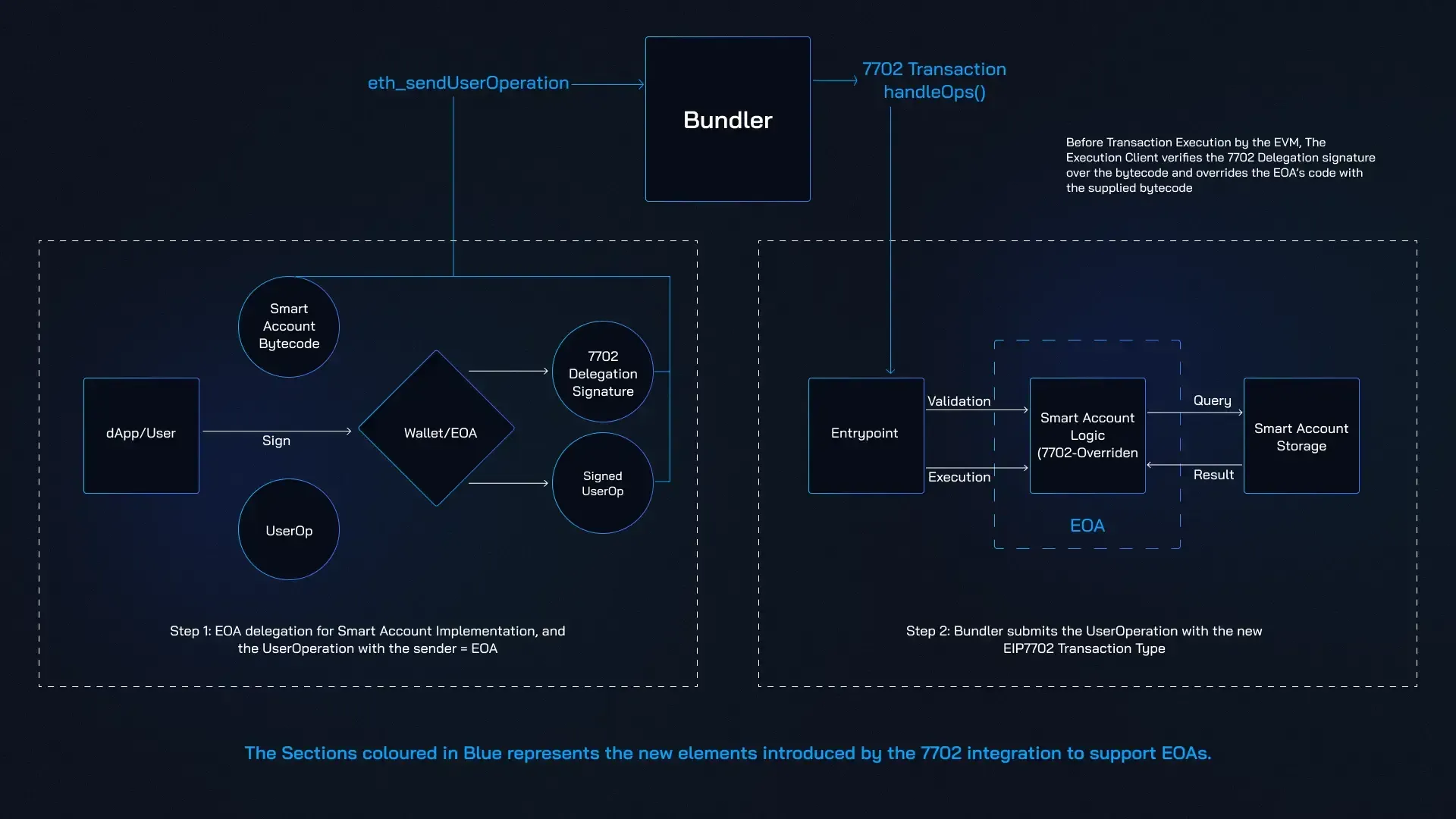
Introduction & Community Reaction
EIP-7702, unveiled as part of the Pectra upgrade, has been met with both enthusiasm and scrutiny within the Ethereum ecosystem. The proposal was developed to address specific needs for scaling and enhancing Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs), which has generated significant interest and debate:
- Community Amazement: The speed and efficiency with which Buterin crafted EIP-7702 has been widely praised, reflecting his deep understanding of Ethereum’s needs and his ability to deliver impactful solutions swiftly.
- Criticisms and Concerns: Following the release of EIP-7702, some members of the Ethereum community expressed concerns about its compatibility with earlier proposals, particularly EIP-4437. While EIP-3074 received mixed reviews, EIP-7702 was seen as a potential alternative that might address some of the shortcomings and concerns associated with the earlier proposal.
Key Features of EIP-7702
EIP-7702 introduces several innovative features designed to enhance EOAs and improve transaction efficiency on the Ethereum network. Here’s a breakdown of these key features:
- Temporary Smart Contract Conversion: One of the standout features of EIP-7702 is its ability to temporarily convert EOAs into smart contract wallets during transaction execution. This conversion unlocks additional functionalities typically available only to smart contracts, such as enhanced programmability and customization, without permanently altering the nature of EOAs. This flexibility allows users to benefit from smart contract features while retaining the core simplicity of EOAs.
- Transaction Batching: EIP-7702 introduces the capability to batch multiple transactions together. This feature significantly boosts efficiency by reducing the number of individual transactions that need to be processed. Batching can also lead to reduced gas fees, making transactions more cost-effective, especially for users performing multiple actions simultaneously.
- Fee Sponsorship: Another major improvement is the introduction of fee sponsorship. This feature allows transactions to be paid for by another account, which can be particularly advantageous for users with limited resources or those participating in sponsored interactions. Fee sponsorship enhances accessibility and can facilitate broader participation in Ethereum-based activities.
- Wallet Privileges: EIP-7702 also outlines mechanisms for managing wallet privileges. This includes the ability to grant limited permissions to specific subkeys, providing users with more granular control over their assets and functions within their wallet. This feature enhances security by allowing users to define and manage access to different aspects of their wallet.
What Makes It Different Than EIP-3074
While both EIP-3074 and EIP-7702 aim to enhance EOAs and improve transaction efficiency, they approach these goals in distinct ways:

- Temporary vs. Permanent Conversion: EIP-3074 allows for the permanent delegation of transaction signing authority to a smart contract (the invoker), which can introduce risks if the invoker is compromised. In contrast, EIP-7702’s temporary conversion of EOAs into smart contract wallets reduces the risk associated with permanent delegation by ensuring that EOAs return to their original state after the transaction. This approach potentially mitigates some of the security concerns raised about EIP-3074.
- Batching and Sponsorship: EIP-7702’s focus on transaction batching and fee sponsorship adds additional layers of efficiency and flexibility, which were not specifically addressed by EIP-3074. These features can help reduce gas costs and increase accessibility for users, further distinguishing EIP-7702’s contribution to Ethereum’s scalability.
- Wallet Privileges: EIP-7702’s ability to manage wallet privileges and permissions provides a more nuanced approach to security and control within the wallet. This feature adds an additional dimension of customization and security that complements the enhancements offered by EIP-3074.
Ending Thoughts
Set to launch in late 2024 or early 2025, the Pectra upgrade is poised to significantly enhance Ethereum's scalability, security, and usability. As developers embrace its features, expect a surge in decentralized applications and Ethereum solidifying its position as the leading smart contract platform.
In essence, Pectra is not just an upgrade; it's a leap towards a more robust, user-friendly, and innovative Ethereum. Whether you're a casual user, a developer, or a stakeholder, Pectra promises to make your Ethereum experience smoother, safer, and more exciting.
With this, Ethereum is going to reach heights it has never before. While you go through all the EIPs, make sure to touch some grass :)
Happy Buidling!