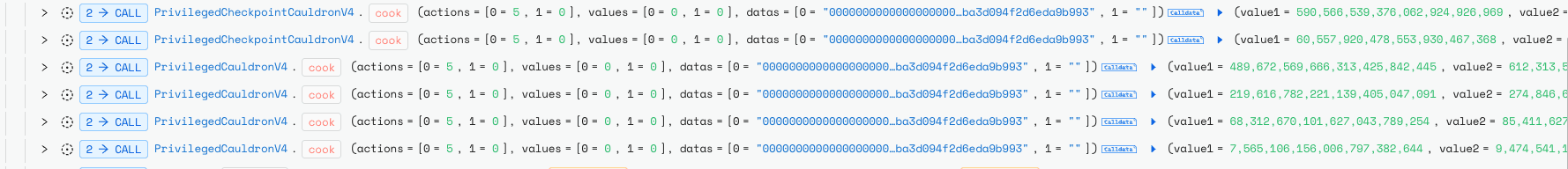
On October 4, 2025, the Abracadabra protocol suffered an exploit targeting its Cauldron V4 contracts, resulting in the theft of approximately 1,793,766 MIM (~$1.8M). The attacker abused a logic flaw in the cook() multi-action flow: Action 5 (borrow) set needsSolvencyCheck = true, but Action 0 reset CookStatus, allowing the final solvency check to be bypassed and enabling under-collateralized borrowing.
Although these contracts were deprecated, they remained active and had not undergone recent audits, leaving the vector open. The attacker drained funds, routed them through Curve and Uniswap into ETH, and later obfuscated proceeds via Tornado Cash.
Hack Analysis
The cook() function enables execution of multiple operations, structured as an array of uint8 actions, where each unit value corresponds to a specific action.
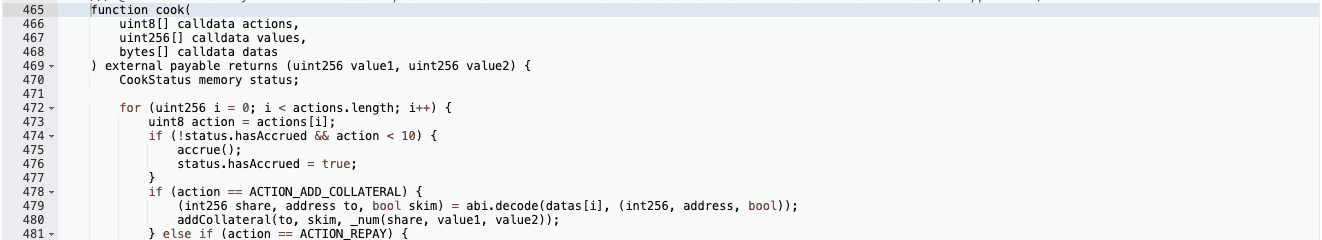
Action 5 is used to borrow assets, which sets CookStatus.needsSolvencyCheck = true . This indicates that, after the action, the protocol must verify whether sufficient collateral has been provided.

Action 0 creates a new action but simply returns an empty CookStatus . This effectively resets the solvency check, removing the requirement to validate collateral for the borrowed asset.

The attacker exploited this mechanism by repeatedly alternating between these actions, ultimately draining 1,793,766 MIM tokens (~$1.8M).
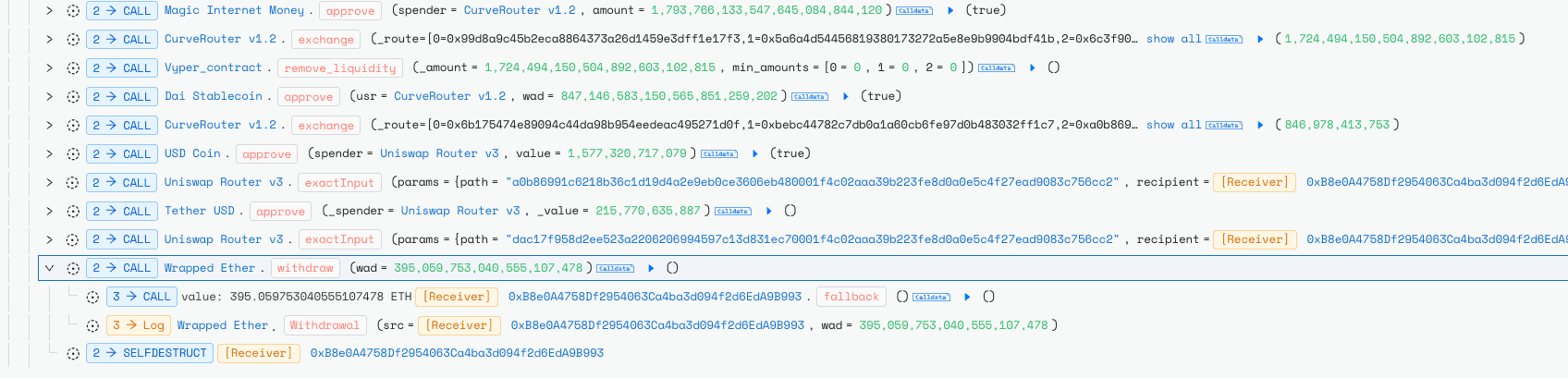
The stolen funds were then laundered through Curve to stablecoins, and later swapped for ETH on Uniswap.
Root Cause
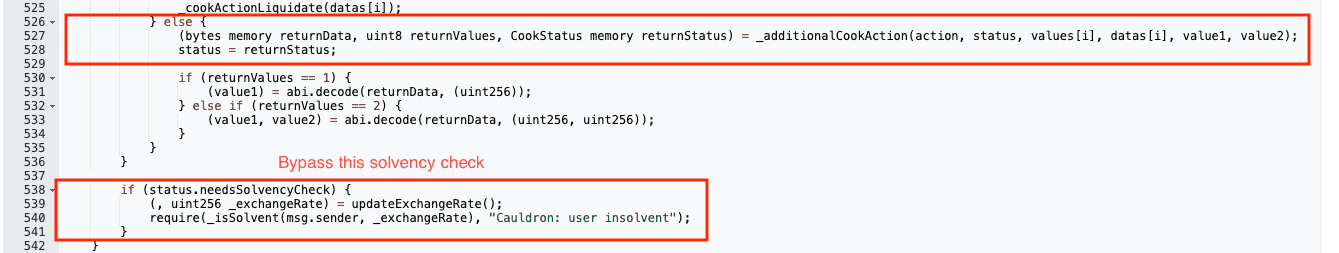
The core vulnerability was a logic error in the cook() function's handling of the shared CookStatus struct. While Action 5 sets needsSolvencyCheck to true during borrowing, Action 0 resets the entire struct via _additionalCookAction(), which is defined as:
function _additionalCookAction(CookStatus memory, bytes memory) internal pure returns (CookStatus memory) {
return CookStatus(false);
}
This reset allows bypassing the final solvency check (_isSolvent(msg.sender, _exchangeRate)). The contracts were deprecated but not deactivated, and no audits had been conducted on the base CauldronV4 since November 2023, as focus shifted to new features.
Funds Flow After Attack
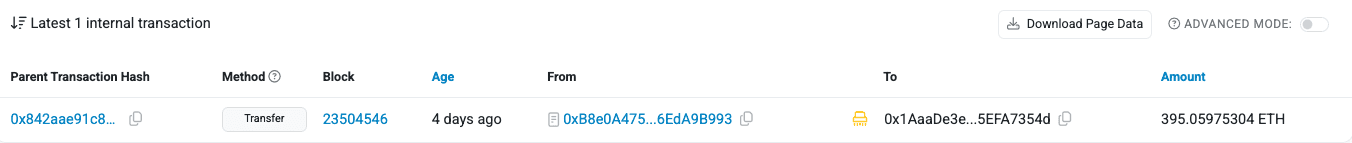
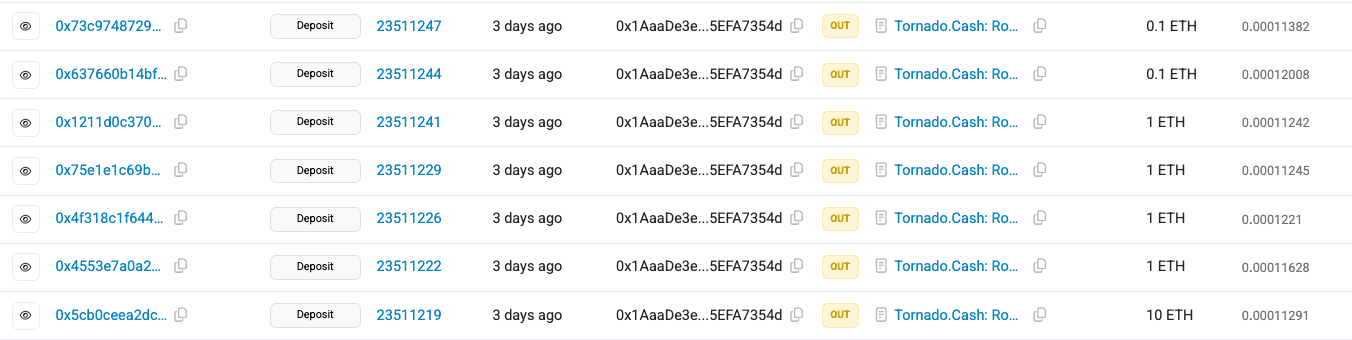
Following the exploit, the attacker obtained 395 ETH, which was subsequently laundered through Tornado Cash across 46 separate transactions.
Post Attack Mitigation
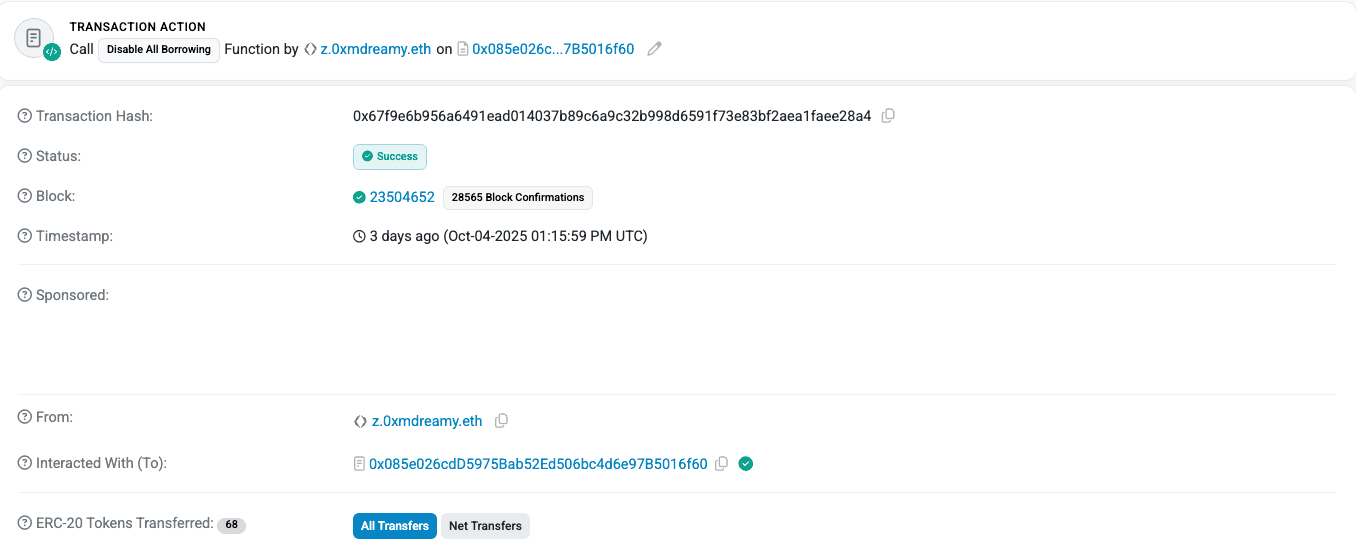
Abracadabra mitigated the incident by immediately pausing all borrowing from the Cauldron contracts.
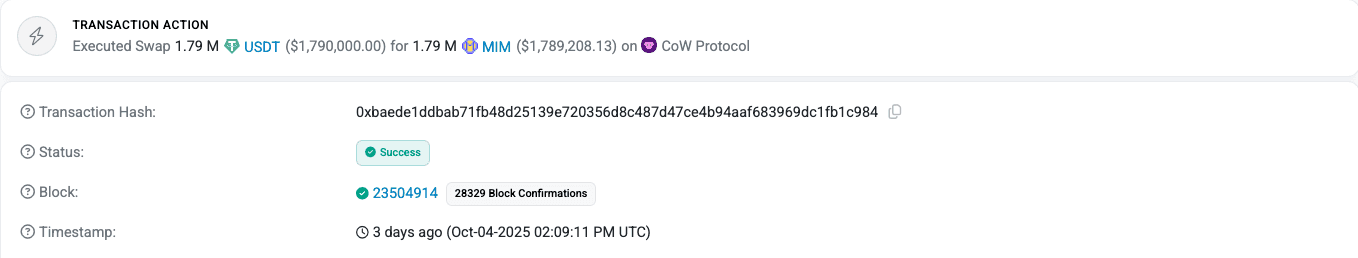
To address the market impact, the DAO treasury repurchased the dumped MIM from secondary markets, claiming that the attack’s effects were fully neutralized. The team confirmed that no user funds were affected, and the overall impact was described as minimal.
Relevant Address and Transactions
- Primary Attacker Address: 0x1aaade3e9062d124b7deb0ed6ddc7055efa7354d
- Attack Contract (Self-Destructed): 0xb8e0a4758df2954063ca4ba3d094f2d6eda9b993
- Exploited DegenBox: 0xd96f48665a1410c0cd669a88898eca36b9fc2cce
- Exploited Cauldrons:
- Key Transactions:
- Attack Transaction: 0x842aae91c89a9e5043e64af34f53dc66daf0f033ad8afbf35ef0c93f99a9e5e6
- Buyback Transaction: 0xbaede1ddbab71fb48d25139e720356d8c487d47ce4b94aaf683969dc1fb1c984
Conclusion
The Abracadabra hack highlights the risks of leaving deprecated contracts active without proper audits or deactivation, especially in a protocol with a history of vulnerabilities. While the $1.8 million loss was mitigated through DAO buybacks and had no direct user impact, it underscores the need for rigorous security practices in DeFi. Lessons include prioritizing security audits for legacy code, implementing fail-safes for status resets in multi-action functions, and swift deactivation of unused components. Abracadabra maintains $154 million in TVL and plans continued development, but repeated incidents could erode user trust.